Students in order to generate new theory will require analyzing the previous hypothesis. Difference between inductive and deductive reasoning business physics methodologyOur MantraInformation is OpportunityKnowledge is PowerBe Inform.
 What Is The Difference Between Inductive Deductive Reasoning Business Physics Methodology Youtube
What Is The Difference Between Inductive Deductive Reasoning Business Physics Methodology Youtube
Deductive reasoning is the most fundamental form of valid reasoning.
Comparison of inductive and deductive reasoning. The paper focuses on the teaching of science and technical courses in High Schools. Inductive reasoning is an activity that is necessary for solving problems in everyday life or carrying out debates while deductive reasoning is crucial in scientific demonstrations and discoveries. The scientific researchers use the deductive method to test theories and hypotheses.
Researchers use such a type of research approach when they have no idea about research results. Inductive reasoning on the other hand is contrary to deductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning is distinct from deductive reasoning.
This article is categorized under. Uses facts rules and deffinitions or properties to arrive at a conclusion deductive. 6 virtual presentation tools thatll engage your audience.
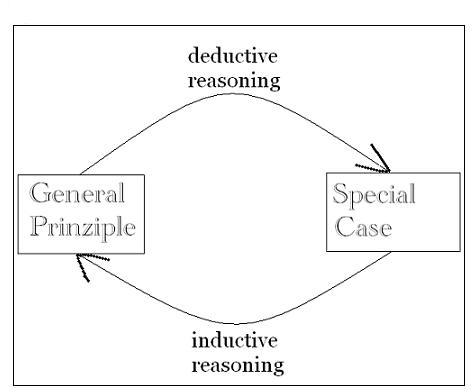
Deductive reasoning uses available facts information or knowledge to deduce a valid conclusion whereas inductive reasoning involves making a generalization from specific facts and observations. Inductive reasoning moves from specific to general. Unlike deductive reasoning moves from general to particular.
Deductive reasoning or deduction initiates with a general statement or hypothesis and examines the possibilities to reach a specific logical conclusion. Inductive reasoning seeks lane generalizations from specific observations. A number of new research directions in this field are identified including comparisons of inductive and deductive reasoning the identification of common core processes in induction and memory tasks and induction involving category uncertainty.
As opposed in deductive reasoning the generalisation made are necessarily true if the premises are correct. This paper discusses two types of reasoning deductive and inductive reasoning. None of these happen in a vacuum or on their own we need both to advance as a species and the process of scientific exploration is one of re-iteration of these methods.
Deductive reasoning is a logical. According to California State University deductive reasoning or inference begins with a general argument or theory and explores the possibilities to. If the premises are correct the conclusion of a deductive argument is certain.
How videos can drive stronger virtual sales. It explores cases of science and mathematical teaching in schools. It is research that researchers use for performing qualitative research.
In inductive reasoning the inferences drawn are probabilistic. In contrast the truth of the conclusion of an inductive argument is probable based upon the evidence given. You can use an inductive research approach for developing a new Hypothesis.
Comparison of inductive and deductive reasoning. The implications of induction research for areas as diverse as complex decision-making and fear generalization are discussed. The paper utilizes cognitive research to discuss given cases of these two types of reasoning.
The main difference between inductive and deductive reasoning is that while inductive reasoning begins with an observation supports it with patterns and then arrives at a hypothesis or theory deductive reasoning begins with a theory supports it with observation and. Here we describe Inductive Deductive Reasoning. Inductive uses patterns to arrive at a conclusion inductive vs.
Reasoning in which the premises are viewed as supplying strong evidence for the truth of the conclusion. Following is a list for comparison between inductive and deductive reasoning.
By nature inductive reasoning is more open-ended and exploratory especially during the early stages. This organization has been experiencing low productivity and errors in communication in the workplace.
 File Inductive And Deductive Reasoning In The Scientific Method Svg Wikimedia Commons
File Inductive And Deductive Reasoning In The Scientific Method Svg Wikimedia Commons
You do this by performing experiments and testing your theory.

Inductive and deductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning by its very nature is more open-ended and exploratory especially at the beginning. Deductive reasoning Where inductive thinking uses experience and proven observations to guess the outcome deductive reasoning uses theories and beliefs to rationalize and prove a specific conclusion. Once you have a theory youll want to test it to see if its valid and your conclusions are sound.
Deductive reasoning is more narrow in nature and is. Unlike inductive reasoning deductive reasoning allows for certainty as long as certain rules are followed. This is one of the many videos in the courseplaylist in Mathematics in th.
Hence deductive reasoning predicts implication-based hypothesis on the effects of a particular scenario unlike inductive reasoning which first takes observations and then runs into a collective. In inductive reasoning we look for patterns to formulate a hypothesis whereas in deductive reasoning we formulate the hypothesis and see if its confirmed by observation. In order to use deductive reasoning you have to have a theory to begin with.
PHI 2103 Rasmussen College Deductive and Inductive Reasoning PPT. What is Deductive Reasoning. Inductive reasoning moves from specific to general.
As opposed in deductive reasoning the. It begins with specific instances EvidenceExamplesDetails and it ends with a generalisation General Conclusion General Conclusion Probable Not definite It can be changed as the specific. Deductive Inductive Reasoning Inductive reasoning uses patterns to arrive at a conclusion conjecture Deductive reasoning uses facts rules definitions or properties to arrive at a conclusion.
The main difference between inductive and deductive reasoning is that while inductive reasoning begins with an observation supports it with patterns and then arrives at a hypothesis or theory deductive reasoning begins with a theory supports it with observation and. The method behind deductive reasoning. Lets have a look at them in more detail.
The goal of inductive reasoning is to predict a likely outcome while the goal of deductive reasoning to prove a fact. You are a Training Specialist hired by Universal Medical Supplies Inc. Deductive reasoning goes in the same direction as that of the conditionals and links premises with conclusionsIf all premises are true the terms are clear and the rules of deductive logic are followed then the conclusion reached is necessarily true.
This video lectures about Problem Solving using Inductive and Deductive Reasoning. In inductive reasoning the inferences drawn are probabilistic. Deductive reasoning also deductive logic is the process of reasoning from one or more statements premises to reach a logical conclusion.
In inductive reasoning the argument supporting the conclusion may or may not be strong. On the contrary in deductive reasoning the argument can be proved valid or invalid. In short inductive reasoning goes from observation to theory while deductive reasoning goes from theory to confirmation.
Unlike deductive reasoning moves from general to particular. Evaluating the Truth of a Premise A formal argument may be set up so that on its face it looks logical. As part of an ongoing professional development series the Vice President of the Human Resources department has tasked you with.
Most social research however involves both inductive and deductive reasoning throughout the research process. However no matter how well-constructed the argument is. So inductive reasoning usually comes before deductive in your research process.
Deductive reasoning is more narrow and is generally used to test or confirm hypotheses.
In its purest form this type of reasoning occurs by analyzing unbiased observations and discovering common patterns. Here is an example.
 Inductive Vs Deductive Reasoning Useful Differences Between Inductive Deductive Reasoning 7esl
Inductive Vs Deductive Reasoning Useful Differences Between Inductive Deductive Reasoning 7esl
Also referred to as cause-and-effect reasoning inductive reasoning can be thought of as a bottom up approach.

What is inductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning is a method of drawing a probable conclusion from an emerging configuration of data. Inductive reasoning tests are one of a range of psychometric tests often used during the recruitment process and are considered one of the more challenging aptitude tests. Patterns resemblances and regularities in experience premises are observed in order to reach conclusions or to generate theory.
Inductive reasoning is a logical process in which multiple premises all believed true or found true most of the time are combined to obtain a specific conclusion. Inductive reasoning or inductive logic is a type of reasoning that involves drawing a general conclusion from a set of specific observations. In this type of inductive reasoning a situation is presented you look at evidence from past.
Types of inductive reasoning Inductive generalization. Using inductive reasoning means using logical thinking to make a prediction or forecast behavior based on previous patterns. Inductive reasoning is the act of using specific scenarios and making generalized conclusions from them.
Definition of Inductive Reasoning In research inductive reasoning alludes to the logical process in which specific instances or situations are observed or analysed to establish general principles. Inductive reasoning is based on learning from experience. Inductive reasoning or induction is the process of using past experiences or knowledge to draw conclusions.
This type of inductive reasoning utilizes statistical data to draw conclusions. Of course your reasoning needs to be backed up by credible data in order to reach a rational conclusion but using this logic can usually get you a good understanding of whats going on. Inductive reasoning A logical process where multiple premises that are true or true most of the time are combined to form a conclusion.
The term inductive reasoning refers to reasoning that takes specific information and makes a broader generalization thats considered probable while still remaining open to the fact that the conclusion may not be 100 guaranteed. What Is Inductive Reasoning. Inductive reasoning is a strategy for reasoning where the premises are providing some proof for the reality of the end.
It gathers different premises to provide some evidence for a more general conclusion. In this process the multiple propositions are believed to. In both cases youre making a conclusion based on an observation of what has happened.
Application of Inductive Approach Inductive Reasoning in Business Research. Inductive reasoning is often used in applications that involve prediction forecasting or behavior. In the example above notice that 3 is added to the previous term in order to get the current term or current number.
Lets go back to the example I stated at the beginning of the video and turn it into some inductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning is a type of logical thinking that involves forming. Inductive reasoning can be especially helpful when youre trying to make predictions or find trends.
2 rows Updated June 26 2020. The logical conclusion we can make based on this pattern is that to find all the numbers after 12 just. What Is Inductive Reasoning.
Some people think of inductive reasoning as bottom-up logic because it involves widening specific premises out into broader generalizations. Often used in prediction and forecasting. Inductive reasoning is making conclusions based on patterns you observeThe conclusion you reach is called a conjecture.