Sampling in market research is of two types probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Restricted random sampling A Simple random sampling Unrestricted random sampling A simple random sampling is one in which every item of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
 Types Of Sampling Exam Nights Live
Types Of Sampling Exam Nights Live
Cluster Random Sampling This is one of the popular types of sampling methods that randomly select members from a list which is too large.

Kinds of random sampling. You can then randomly generate a number for each element using Excel for example and take the. Random Sampling Examples of Different Types Types of Random Sampling. More specifically it initially requires a sampling frame a list or database of all members of a population.
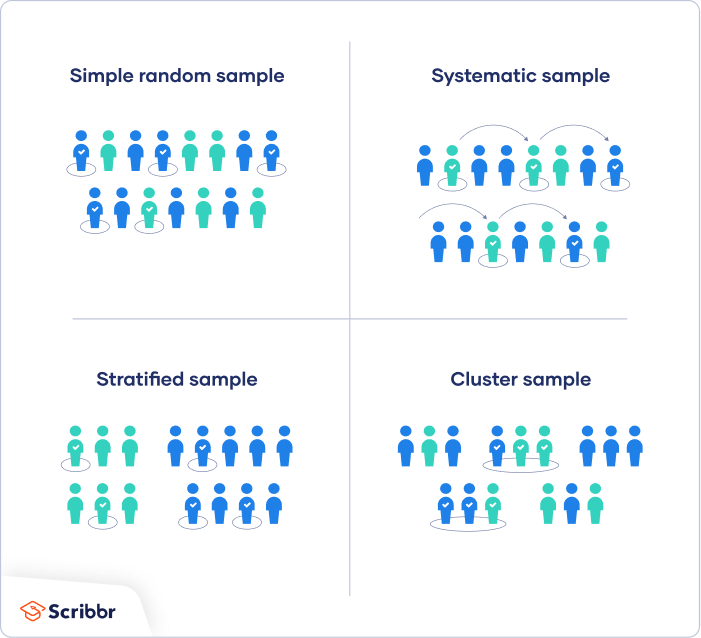
The four types of random sampling techniques are simple random sampling systematic sampling stratified random sampling and cluster random sampling. Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling systematic sampling stratified sampling and cluster sampling. Time effort and money.
Multiple types of randomness can be included to reduce researcher bias. Random samples are the best method of selecting your sample from the population of interest. The advantages are that your sample should represent the target population and eliminate sampling bias.
The disadvantage is that it is very difficult to achieve ie. Simple random sampling requires using randomly generated numbers to choose a sample. Here the selection of items entirely depends on luck or probability and therefore this sampling technique is also sometimes known as a method of chances.
The two types of sampling are random sampling and nonrandom sampling. Every person in the pool has the same likelihood that you will choose them. The primary types of this sampling are simple random sampling stratified sampling cluster sampling and multistage sampling.
This method is also known as unrestricted random sampling. It is important to know the distinctions between the different types of samples. Types of sampling RANDOM SAMPLING NON RANDOM SAMPLIG 7.
What is simple random sampling. Consider a lottery method. Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or.
In the sampling methods samples which are not arbitrary are typically called convenience samples. There are two common approaches that are used for random sampling to limit any potential bias in the data. There are 4 types of random sampling techniques.
Researchers may also use computer programs that generate random numbers. Probability sampling is a sampling technique where a researcher sets a selection of a few criteria and chooses members of a population randomly. Use an imperfect method and you risk.
As youd guess by the name this is the most common approach to random sampling. Simple or unrestricted random sampling. RANDOM SAMPLING The term random means that each unit individualin the selected population has the equal chance of selection and selection of one individual in no way affects selection of another individual.
Types of Random Sampling Methods 1. The researcher identifies the different types of people that make up the target. Cluster sample A cluster sample involves using a simple random sample of evident groups that the population contains.
You can place all possible respondents in a pool and randomly or blindly select participants. Nonrandom sampling uses some criteria for choosing the sample whereas random sampling does not. Stratified sample - A stratified sample results when a population is split into at least two non-overlapping sub-populations.
The first is a lottery method which involves having a population group drawing to. Simple random sampling is defined as a sampling technique where every item in the population has an even chance and likelihood of being selected in the sample. Simple random sampling or SRS occurs when each sample participant has the same probability of being chosen for the study.
Lets take a closer look at these two methods of sampling. Methodology is vital to getting a truly random sample. A typical example is when a researcher wants to choose 1000 individuals from the entire population of the US.
Systematic sampling is the selection of specific individuals or members from an entire. There are two types of random sampling. Simple random sampling is a type of probability sampling in which the researcher randomly selects.
After selecting the clusters either complete clusters will be used for the study or apply the other sampling methods to pick the sample elements from the clusters. Steps involved in cluster sampling.
 Sampling Methods Simply Psychology
Sampling Methods Simply Psychology
This is similar to the national lottery.
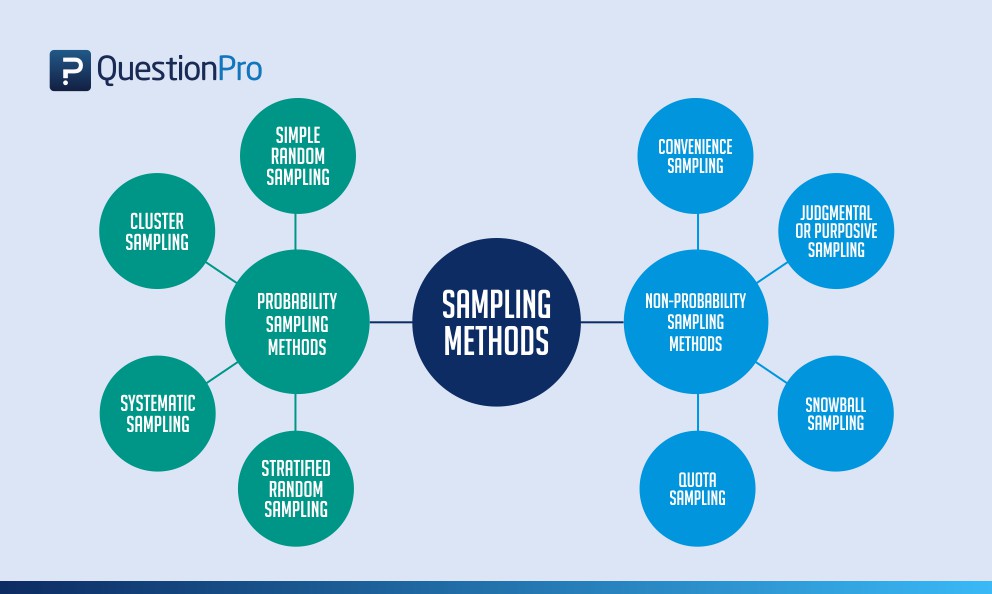
All sampling methods. First a determination must be made of what behaviors to measure. Each of these methods includes different types of techniques of sam pling. There are various sampling methods.
Perhaps the worst types of sampling methods are convenience samples and voluntary response samples. Convenience sampling and voluntary response sampling Convenience sampling is the practice of samples chosen by selecting whoever is convenient. There are two basic types of sampling methods.
A sample cluster is selected using simple random sampling method and then survey is conducted on people of that sample cluster. Probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Cluster sampling - In this type of sampling method each population member is assigned to a unique group called cluster.
Create the clusters from the population data. Types of sampling methods namely. There are several different sampling techniques available and they can be subdivided into two groups.
Data Scientist does a vast analysis of the data and therefore these methods help them to know insights of the data sample and its effect. There are four types of probability sampling techniques. What is probability sampling.
The concept like parameter statistic sampling errors precision variable sampling frame sampling design etc. We hope you liked the article on Types of Sampling Method. A list of all the elements from a population is known as the sampling frame.
As a researcher you should know these sampling techniques before trying to accumulate sample data. Topics include populations census sample surveys sampling units sampling frames Random Sampling Systematic Sampling Stratified sampling and Quota sampling A population is a group that we want to find information about. In simple words probability sampling also known as random sampling or chance sampling utilizes random sampling techniques and principles to create a sample.
Multistage sampling - In such case combination of different sampling methods at different stages. It might be a group of people or it could be simply a group of numbers. For instance you are selecting a telephone directory of students or a list of social media users.
Select each cluster as a sampling frame. Sampling Size Sampling Frame. Cluster sampling is a method where the researchers divide the entire population into sections or.
Our mission is to provide a free world-class education to anyone anywhere. Are used in sample and sample design. This is the currently selected item.
There are numerous ways of getting a sample but here are the most commonly used sampling methods. Sampling Frame Vs. If the behaviors are few and easily measured then All Occurrences Sampling is the method of choice because it generates accurate frequency and duration data through continuous.
Probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Voluntary response sampling is allowing the sample to volunteer. All these are sampling methods.
In probability random sampling you start with a complete sampling frame of all eligible individuals from which you select your sample. The purest form of sampling under the probability approach random sampling provides equal chances of being picked for each member of the target population. Types of studies experimental vs.
Answering questions related to several variables assists in narrowing the choices of sampling methods. The following sampling methods are examples of probability sampling methods. Select the random clusters.
Simple Random Sampling SRS Stratified Sampling. The one chosen will depend on a number of factors such as time money etc. Random sampling is a type of probability sampling where everyone in the entire target population has an equal chance of being selected.
Theory of Sampling Sampling theory is a study of relationship between samples and population. Simple Random Sampling SRS When looking at probability sampling methods simple random sampling is a special case of a random sample. One of the best probability sampling techniques that helps in saving time and resources is the.
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which a random sample from a larger population is selected. It is a probability sampling method.
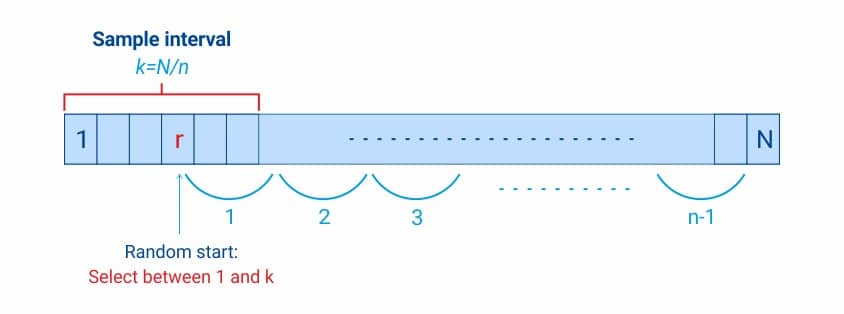 Systematic Sampling Definition Examples And Types Questionpro
Systematic Sampling Definition Examples And Types Questionpro
Systematic sampling is an extended implementation of the same old probability technique in which each member of the group is selected at regular periods to form a sample.
Define systematic sampling in statistics. Systematic sampling is a statistical method involving the selection of elements from an ordered sampling frame. For example a researcher wants to. Systematic sampling is a technique for creating a random probability sample in which each piece of data is chosen at a fixed interval for inclusion in the sample.
In this approach progression through the list is treated circularly with a return to the top once the end of the list is passed. If the population order is random or random-like eg alphabetical then this method will give you a representative sample that can be used to draw conclusions about the population. Statistical sampling refers to the study of populations by gathering information about and analyzing it.
Statistics a variant of sample 2 3. The Main Characteristics of Sampling. Systematic sampling is a random sampling technique which is frequently chosen by researchers for its simplicity and its periodic quality.
What are the types of systematic sampling. It is the base for a great deal of information ranging from estimates of average height in a nation to studies on the impact of marketing to children. In this method initially the target population needs to be selected even before the selection of participants.
Example of probability sampling. Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which researchers select members of the population at a regular interval or k determined in advance. Then the researcher will select each nth subject from the list.
Linear systematic sampling is a systematic sampling method where samples arent repeated at. In sampling we assume that samples are drawn from the population and sample means and population means are equal. In systematic sampling also called systematic random sampling every Nth member of population is selected to be included in the study.
Instagram wants to determine what proportion of their users are college students. In systematic random sampling the researcher first randomly picks the first item or subject from the population. True or False.
Systematic random sampling is a method to select samples at a particular preset interval. Then samples are selected from each group using simple random sampling method and then survey is conducted on people of those samples. It has been stated that with systematic sampling every Kth item is selected to produce.
How does it Work. Stratified sampling - In this type of sampling method population is divided into groups called strata based on certain common characteristic like geography. Begin with a positive whole number k.
Definition of a Systematic Sample A systematic sample is obtained by a very straightforward process. Theres an civil right for each member of a population to be selected using this sampling technique. Theres an equal opportunity for every member of a population to be selected using this sampling technique.
Systematic Sampling can be used by statisticians in case they want to save time or are dissatisfied with the results. It helps us to make statistical inferences about the population. Look at our population and then select the k th element.
Systematic sampling is an extended implementation of an equivalent old probability technique during which each member of the group is chosen at regular periods to make a sample. Systematic Sampling is sampling in which data is obtained by selecting every kth object. Statistics the process of selecting a random sample 2.
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which a random sample with a fixed periodic interval is selected from a larger population. The most common form of systematic sampling is an equiprobability method. Sampling is a statistical procedure that is concerned with the selection of the individual observation.
There are several different purposive sampling types that researchers can use to collect their information. Since there are several different types of purposive sampling eg.
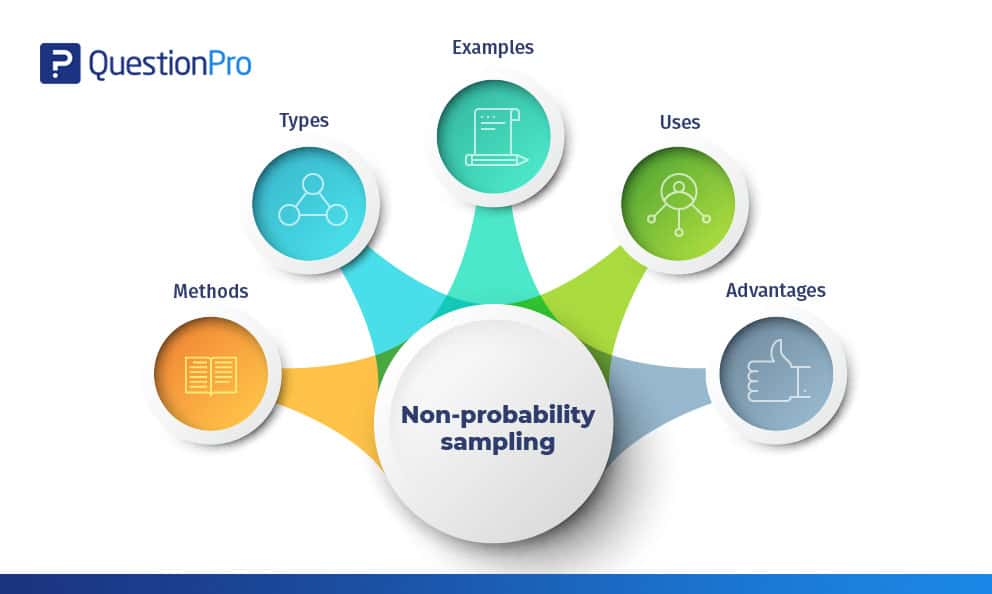 Non Probability Sampling Definition Types Examples And Advantages Questionpro
Non Probability Sampling Definition Types Examples And Advantages Questionpro
Purposive Sampling Used in Ethnobotanical Atudies.
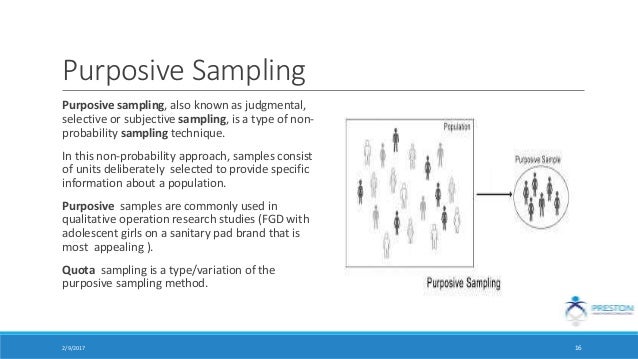
7 types of purposive sampling. Getting a second opinion. In purposive sampling personal judgment needs to be used to choose cases that help answer research questions or achieve research objectives. Purposive sampling is an acceptable kind of sampling for special situations.
Purposive or Judgmental Sample i. In purposive sampling the researcher chooses voluntarily the elements that will make up the sample assuming that it will be representative of the reference population. Explains cases that are average and normal.
1 Advantages of Purposive Sampling. Heterogeneous or Maximum Variation Homogenous Typical Case Sampling Deviant or Extreme Critical Case Sampling Expert Total Population. As you can imagine their feedback may be very different from the opinion.
We feel that large numbers of studies can threaten the quality of the analysis in a qualitative evidence synthesis. What are the types of Purposive Sampling method as used in Statistics. The aim of this paper is to outline the nature and intent of purposive sampling presenting three different case studies as examples of its application in different contexts.
Purposive sampling is used most often when a difficult-to-reach population needs to be measured. Each of these types of purposive sampling technique is discussed in turn. Some types of research design necessitate researchers taking a decision about the individual participants who would be most likely to contribute appropriate data both in terms of relevance and depth.
Maximum variation sampling Homogeneous sampling Typical case sampling Extreme or deviant case sampling Critical case sampling Total population sampling Expert sampling. Studies of specific skills knowledge or practices Research Problem Methods Population Sampled Sample Analyses Citation Cultural significance of plants Unstructured interviews. For example in life history research some potential.
Judgmental sampling is completely opposite of probability sampling such as simple random sampling stratified sampling systematic sampling cluster sampling. Among various types of sampling method purposive sampling is also one of them. Extreme or deviant case.
Studies of specific skills knowledge or practices. Snowball or Chain Sampling. An example that will be familiar to psychology students is the use of students as opinion samples by university professors.
Wide range of techniques. Four aspects to this concept have previously been described. Purposive sampling also knows as judgmental selective or subjective sampling reflects group of sampling techniques that rely on the judgment of the researcher.
This sampling procedure is always prefer the choice of the researcher. Credibility transferability dependability and confirmability. Homogenous sampling expert sampling critical case sampling etc one of the key benefits of this sampling method is the ability to gather large amounts of information by using a range of different techniques.
Survivorship bias occurs when your survey is limited to customers clients and employees who have remained with you over time. Deriving samples from cases that are perceived as unusual or rare such as. Cell Phone Only Household.
Following are the main types of purposive sampling. We employed a sampling strategy as seventy-nine studies were eligible for inclusion in the synthesis. We used purposive sampling to select 38 primary studies for the data synthesis using a three step-sampling frame.
Lets take a closer look at these two methods of sampling. It is a type of purposive sampling in which the whole universe is divided first into certain parts. It uses the judgment of an expert in selecting cases or it selects cases with a specific purpose in mind.
Sampling in market research is of two types probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Seven Types of Purposive Sampling A maximum variationheterogeneous purposive sample is one which is selected to provide a diverse range of cases relevant. Sampling Coverage And Weighting.
Types of Purposive Sampling. Purposive Sampling Types Maximum VariationHeterogeneous Purposive Sample Homogeneous Purposive Sample Typical Case Sampling ExtremeDeviant Case Sampling Critical Case Sampling Total Population Sampling Expert Sampling. According to the type of cases purposive sampling can be divided into the following six categories.
A homogeneous purposive sample is one that is selected for having a shared characteristic or set of characteristics. Probability sampling is a sampling technique where a researcher sets a selection of a few criteria and chooses members of a population randomly.