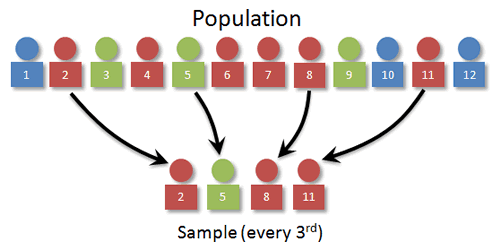
For example if a researcher wanted to create a systematic sample of 1000 students at a university with an enrolled population of 10000 he or she would choose every tenth person from a list of all students. Understanding Sampling Random Systematic Stratified and Cluster 17082020 17082020 By NOSPlan Blog Note This article focuses on understanding part of probability sampling techniques through story telling method rather than going conventionally.
Systematic random sampling Systematic random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique see our article Probability sampling if you do not know what probability sampling is.
Systematic random sampling definition. Like simple random sampling systematic sampling is a type of probability sampling where each element in the population has a known and equal probability of being selected. The counterpart of this sampling is Non-probability sampling or Non-random sampling. Systematic sampling involves the use of a rational approach to picking a sample from a population.
If employed with care the systematic sampling design simplifies much of the work involved in simple random sampling or stratified sampling. Simple random sampling is defined as a sampling technique where every item in the population has an even chance and likelihood of being selected in the sample. Below are the example steps to set up a systematic random sample.
Systematic sampling is a method that imitates many of the randomization benefits of simple random sampling but is slightly easier to conduct. For example Lucas can. Systematic sampling is a technique for creating a random probability sample in which each piece of data is chosen at a fixed interval for inclusion in the sample.
Systematic random sampling is a method to select samples at a particular preset interval. Random sampling is a method of choosing a sample of observations from a population to make assumptions about the population. Systematic sampling is one method in the broader category of random sampling for this reason it requires precise control of the sampling frame of selectable individuals and of.
As a researcher select a random starting point between 1 and the sampling interval. When we make this substitution we must be certain that the method we use for our sample. In systematic random sampling the researcher first randomly picks the first item or subject from the population.
The Systematic Sampling is yet another probability sampling technique wherein the starting point from where the element is to be drawn from the population is chosen randomly and then the subsequent items are selected on the basis of the fixed periodic interval between the sample items. Systematic sampling is more or less a method that involves the selection of various elements that are ordered from a sampling frame and taking this statistical procedure starts from the random selection of elements that belongs to a list and then every sampling interval from the frame is selected and this method of sampling can only be applied if at all the given population is. Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which a random sample with a fixed periodic interval is selected from a larger population.
Here the selection of items entirely depends on luck or probability and therefore this sampling technique is also sometimes known as a method of chances. A systematic sample that is also random is referred to as a systematic random sample. Systematic sampling is a random sampling technique which is frequently chosen by researchers for its simplicity and its periodic quality.
The usual technique is to begin sampling at a random point in the population and then make additional selections at a predetermined interval. In such instances a more simplified and versatile form of probability sampling design known as systematic sampling can be employed. Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population.
Alphabetically or by address is still likely to produce a more representative sample than something like snowball sampling or opportunity sampling. You can use systematic sampling with a list of the entire population as in simple random sampling. It is also called probability sampling.
The most representative samples from this method are achieved when the sampling frame list is randomised this is known as systematic random sampling although the quasi-random sampling of picking every nth person however it is listed eg. First calculate and fix the sampling interval. With the systematic random sample there is an equal chance probability of selecting each unit from within the population when creating the sample.
This type of random sample can sometimes be substituted for a simple random sample.