The points presented to you describe the differences between internal and external validity. In other words it is the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized to and across other situations people stimuli and times.
 Internal And External Validity
Internal And External Validity
Internal validity we are making the experiment more and more artificial and thereby its generalizability external validity suffers.

Internal validity and external validity. External validity examines whether the study findings can be generalized to other contexts. External validity and internal validity often conflict Cozby 2014. Since internal validity is based on a cause and effect relationship between specified variables if that is what the researcher seeks to identify then there is a strong case for establishing internal validity Cozby 2014.
The concept of validity is also applied to research studies and their findings. For laboratory experiments with tightly controlled conditions it is usually easy to achieve high internal validity. When you claim high internal validity.
External and Internal Validity. Another difference between the two is that internal validity emphasizes the relationship. Below is a selection of external threats that can help guide your conclusions on the generalizability of your research results.
The degree which a studys results are generalizable to other subjects settings andor behaviors not included in the original study. Because general conclusions are almost always a goal in. Internal validity is a level up to which causal relationships between variables are trustworthy.
In contrast internal validity is the validity of conclusions drawn within the context of a particular study. Internal Validity the degree to which the results are attributable to the independent variable and not some other rival explanation. This is about the validity of results within or internal to a study.
The balance technique would allow for more generalizability than would the eliminate or hold constant techniques. External validity refers to the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized to other settings ecological validity other people population validity and over time historical validity. The validity of your experiment depends on your experimental design.
I nternal validity is the degree of confidence that the causal relationship you are testing is not influenced by other factors or variables. Internal Validity is nothing but the measure of the accuracy of the experiment. External validity is the extent to which your results can be generalized to other contexts.
However there are several factors that jeopardize both the internal and external validity. Threats to External and Internal Validity. Example in clinical context.
External validity is the validity of applying the conclusions of a scientific study outside the context of that study. Internal validity examines whether the study design conduct and analysis answer the research questions without bias. Health services research it can be difficult to claim high internal validity.
There are two major types of validity. There is the internal and external validity. For studies in difficult to control environments eg.
Difference between internal and external validity. Threats to internal validity are important to recognize and counter in a research design for a robust study. The information needed to determine the internal and external validity of an experimental study is discussed.
On the other hand External validity is a degree up to which research outcome applies to other situations. An exception would be in reference to specific control techniques eg. Establishing the internal validity of a study is based on a logical process.
A behavior analyst is implementing a new intervention from a study that they read in a peer reviewed journal. The strength of assigning causes to outcomes. Threats to internal validity and how to counter them.
Validity is very important in research since it gives meaning to the study. External Validity the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized 7. It usually concerns causality ie.
Internal validity can be improved by controlling extraneous variables using standardized instructions counter balancing and eliminating demand characteristics and investigator effects. The extent to which the experiment is free from errors and any difference in measurement is due to independent variable. Applicability of evaluation results to other populations setting and time periods is often a question to be answered once internal validity threats have been eliminated or minimized.
For example restricting your participants to college-aged people enhances internal validity at the expense of external validity the findings of the study may only be generalizable to college-aged populations. Validity is the extent to which a research study measures what it aims to measure Onwuegbuzie 2000. Internal validity is the degree to which a study establishes the cause-and-effect relationship between the treatment and the observed outcome.
 Internal Versus External Validity Youtube
Internal Versus External Validity Youtube
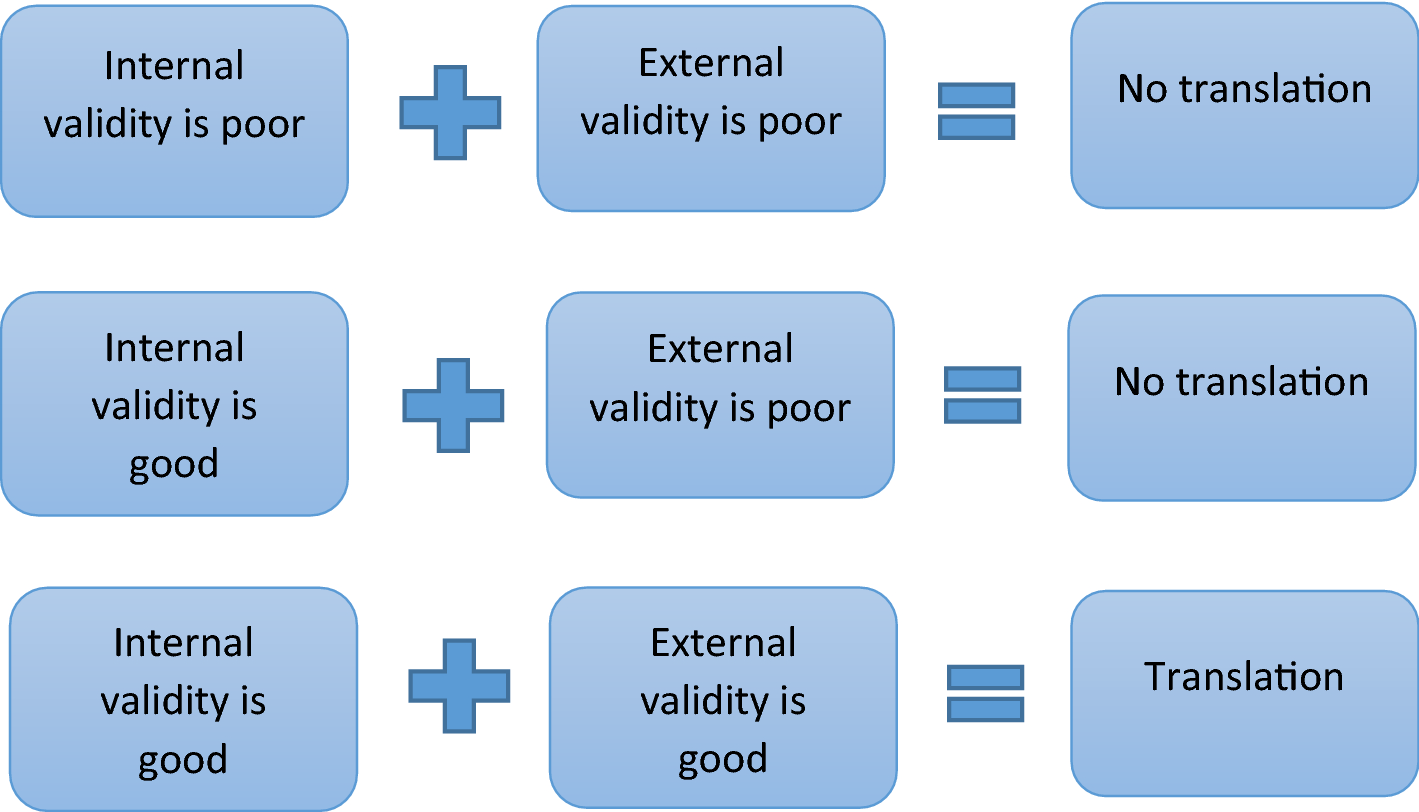 Is It Possible To Overcome Issues Of External Validity In Preclinical Animal Research Why Most Animal Models Are Bound To Fail Journal Of Translational Medicine Full Text
Is It Possible To Overcome Issues Of External Validity In Preclinical Animal Research Why Most Animal Models Are Bound To Fail Journal Of Translational Medicine Full Text
 Threats To Experimental Validity Internal And Exteranl Kawiist Academy
Threats To Experimental Validity Internal And Exteranl Kawiist Academy
 Internal And External Validity By Eion C
Internal And External Validity By Eion C
 Validity And Reliability Of Case Study Research Yin 2003 Download Table
Validity And Reliability Of Case Study Research Yin 2003 Download Table
 Difference Between Internal And External Validity With Comparison Chart Key Differences
Difference Between Internal And External Validity With Comparison Chart Key Differences
 External Validity Internal Validity Flashcards Quizlet
External Validity Internal Validity Flashcards Quizlet
 Internal And External Validity Can You Apply Research Study Results To Your Patients
Internal And External Validity Can You Apply Research Study Results To Your Patients
 The Relationship Between Internal Validity External Validity And Download Scientific Diagram
The Relationship Between Internal Validity External Validity And Download Scientific Diagram
 Internal And External Validity Youtube
Internal And External Validity Youtube
 Image Result For Briefly Define Internal And External Validity External Validity Me On A Map Internal Validity
Image Result For Briefly Define Internal And External Validity External Validity Me On A Map Internal Validity
 Difference Between Internal And External Validity
Difference Between Internal And External Validity
 External Validity Elite Institute
External Validity Elite Institute
/internal-and-external-validity-4584479_final-a1cf2c26ce464856bb86fe5ceb99b17b.png) Understanding Internal And External Validity
Understanding Internal And External Validity